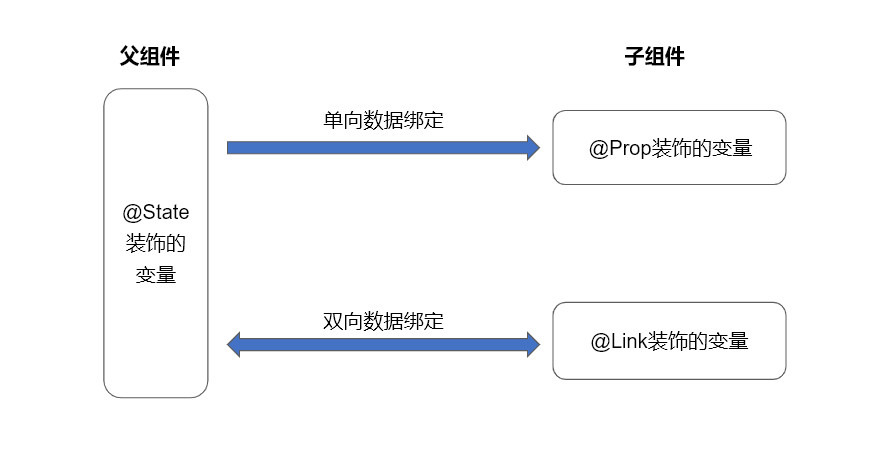
组件级别的状态管理,可以观察组件内变化和不同组件层级的变化,但需要唯一观察同一个组件树上,即同一个页面内。
在状态装饰器中 @State 是最基础的,使变量拥有状态属性的装饰器,也是大部分状态变量的数据源。
基础装饰器
@State 装饰器
所装饰的变量拥有其所属组件的状态,可以作为其子组件单向和双向同步的数据源。当其数值改变时,会引起相关组件的渲染刷新。
@Prop 装饰器
所装饰的变量和父组件建立单向同步关系,允许组件内部修改@Prop装饰的变量,但修改后的数据不会同步到父组件。
需要注意:必须使用其父组件提供的@State变量进行初始化。
@Link 装饰器
所装饰的变量和父组件建立双向同步关系,@Link装饰的变量数据修改后会同步回父组件,父组件的更新也会同步给@Link装饰的变量。
之间的关系
用法示例
示例一:@State 和 @Prop
// 子组件
@Component
struct child {
@Prop count: number
build() {
Column() {
Text('子组件')
.fontSize(40)
.fontColor(Color.White)
Text(`count:${this.count}`)
.fontSize(40)
.fontColor(Color.White)
Button('count增加', { type: ButtonType.Normal })
.fontSize(30)
.padding(12)
.margin({ top: 50 })
.borderRadius(15)
.backgroundColor('#fff')
.fontColor('#ff40c1c1')
.onClick(() => {
this.count++
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('60%')
.backgroundColor('#ff52d0d0')
.margin({ top: 80 })
.padding({ top: 50 })
}
}
// 父组件
@Entry
@Component
struct parent {
@State count: number = 1
build() {
Column() {
Text('父组件')
.fontSize(40)
.fontColor(Color.White)
Text(`count:${this.count}`)
.fontSize(40)
.fontColor(Color.White)
// 子组件
child({ count: this.count })
}
.width('100%')
.height('80%')
.backgroundColor('#8adddc')
.margin({ top: 50 })
.padding({ top: 20 })
}
}
效果:
使用@Prop装饰的变量,修改后并不会同步到父组件。
示例二:@State 和 @Link
// 子组件
@Component
struct child {
@Link count: number
build() {
Column() {
Text('子组件')
.fontSize(40)
.fontColor(Color.White)
Text(`count:${this.count}`)
.fontSize(40)
.fontColor(Color.White)
Button('count增加', { type: ButtonType.Normal })
.fontSize(30)
.padding(12)
.margin({ top: 50 })
.borderRadius(15)
.backgroundColor('#fff')
.fontColor('#ff40c1c1')
.onClick(() => {
this.count++
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('60%')
.backgroundColor('#ff52d0d0')
.margin({ top: 80 })
.padding({ top: 50 })
}
}
// 父组件
@Entry
@Component
struct parent {
@State count: number = 1
build() {
Column() {
Text('父组件')
.fontSize(40)
.fontColor(Color.White)
Text(`count:${this.count}`)
.fontSize(40)
.fontColor(Color.White)
// 子组件
child({ count:$count })
}
.width('100%')
.height('80%')
.backgroundColor('#8adddc')
.margin({ top: 50 })
.padding({ top: 20 })
}
}
效果:
使用@Link装饰的变量,修改后会同步到父组件。
跨层级传递装饰器
@Provide装饰器与@Consume装饰器应用于与后代组件双向同步数据,在多个层级之间传递。
不同于上文提到的父子组件之间通过命名参数机制传递,@Provide和@Consume摆脱参数传递机制的束缚,实现跨层级传递。
需要注意:不允许在同一个自定义组件内,包括其子组件中声明多个同名或者同别名的@Provide装饰的变量
@Provide 装饰器
所装饰的状态变量自动对其所有后代组件可用。方便之处在于,开发者不需要多次在组件之间传递变量。
@Consume 装饰器
后代组件可通过使用@Consume去获取@Provide提供的变量。
用法示例
// 子组件【 D 】
@Component
struct childD {
@Consume count: number
build() {
Column() {
Text('第3层子组件D').fontSize(35)
Row() {
Text(`count:${this.count}`).fontSize(30)
Button('清空', { type: ButtonType.Normal })
.fontSize(24)
.borderRadius(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.count = 0
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding({ top: 24 })
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)
}
.backgroundColor('rgb(121, 187, 255)')
.width('100%')
.height('50%')
.padding(12)
.margin({ top: 50 })
}
}
// 子组件【 C 】
@Component
struct childC {
@Consume count: number
build() {
Column() {
Text('第2层子组件C').fontSize(35)
Row() {
Text(`count:${this.count}`).fontSize(30)
Button('数量x2', { type: ButtonType.Normal })
.fontSize(24)
.borderRadius(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.count *= 2
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding({ top: 24 })
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)
// 第3层子组件
childD()
}
.backgroundColor('rgb(160, 207, 255)')
.width('100%')
.height('80%')
.padding(12)
.margin({ top: 50 })
}
}
// 子组件【 B 】
@Component
struct childB {
build() {
Column() {
Text('第1层子组件B').fontSize(35)
// 第2层子组件
childC()
}
.backgroundColor('rgb(198, 226, 255)')
.width('100%')
.height('80%')
.padding(12)
.margin({ top: 20 })
}
}
// 父组件【 A 】
@Entry
@Component
struct parentA {
@Provide count: number = 5
build() {
Column() {
Text('父组件A').fontSize(35)
Row() {
Text(`count:${this.count}`).fontSize(30)
Button('数量+1', { type: ButtonType.Normal })
.fontSize(24)
.borderRadius(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.count += 1
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding(24)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)
// 第1层子组件
childB()
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.padding(12)
}
}
效果:
父组件嵌套多层子组件情况下,使用跨层级传递的装饰器来装饰变量,无论在父组件还是后代组件中进行变量值修改,都会同步到父组件及后代组件中。
观察嵌套类对象属性装饰器
以上介绍的装饰器仅能观察到第一层的变化,适合非嵌套类的数据进行单双向数据绑定。
在实际应用开发中,应用会根据开发需要,封装自己的数据模型,对于多层嵌套类数据的属性变化是无法观察到的,这时候就需要用到 @Observed/@ObjectLink 。
@Observed 和 @ObjectLink 用于在涉及嵌套对象或数组的场景中进行双向数据同步。
单独使用@Observed是没有任何作用的,需要搭配@ObjectLink使用。
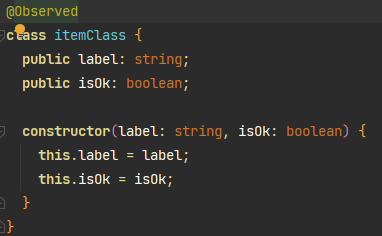
@Observed 类装饰器
装饰 class,需要放在 class 的定义前,数据源使用 new 创建类对象。
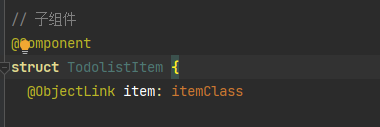
@ObjectLink 装饰器
在子组件中使用 @ObjectLink 装饰器装饰的状态变量,用于接收 @Observed 装饰的类的实例。
注意点:
- 不能在
@Entry装饰的自定义组件中使用; - 装饰的变量是只读的(不能被改变),但变量的属性是可以改变的,如果变量要赋值,请使用
@Prop;
用法示例
@Observed
class classA {
public avatar: string
public nick: string
public status: number
constructor(avatar: string, nick: string, status: number) {
this.avatar = avatar
this.nick = nick
this.status = status
}
}
// 子组件
@Component
struct child {
@ObjectLink item: classA
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
Column() {
Row() {
Image(this.item.avatar)
.width(50)
.width(50)
.borderRadius(90)
Column() {
Text(this.item.nick)
.fontSize(24)
Text(this.item.status ? '已邀请' : '未邀请')
.fontSize(18)
.margin({ top: 8 })
.fontColor(this.item.status ? '#606266' : '#c0c4cc')
}
.margin({ left: 12 })
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)
}
}
Column() {
if (this.item.status) {
Button('取消', { type: ButtonType.Normal })
.borderRadius(12)
.backgroundColor('#909399')
.onClick(() => {
this.item.status = 0
})
} else {
Button('邀请', { type: ButtonType.Normal })
.borderRadius(12)
.onClick(() => {
this.item.status = 1
})
}
}
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.End)
}
.width('94%')
.padding(15)
.backgroundColor('#eee')
.margin({ bottom: 12 })
.borderRadius(15)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)
}
}
}
// 父组件
@Entry
@Component
struct parent {
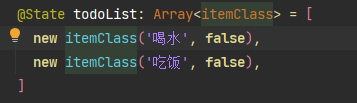
@State list: classA[] = [
new classA(
'https://image.d2school.com/user/avatar/default/others/a.png',
'不息de进步',
0
),
new classA(
'https://image.d2school.com/user/avatar/default/others/d.png',
'无限de仙境',
0
),
new classA(
'https://image.d2school.com/user/avatar/default/others/f.png',
'轻巧de狂澜',
0
),
new classA(
'https://image.d2school.com/user/avatar/default/others/j.png',
'浅红de豪情',
0
),
new classA(
'https://image.d2school.com/user/avatar/default/others/x.png',
'诚实de科学',
1
)
]
build() {
Column() {
Text('好友').fontSize(40).margin(16)
ForEach(this.list, (item) => {
child({ item: item })
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
效果: